Cerebral ischemic diagnosing bases on spontaneity of decreasing and loss memory and vision. And Face Arm Speech Time [FAST] scale. Roles of diagnostic imaging in cerebral ischemia are exactly detecting and rapidly in time (less than one hour).
CASE 01:
A male patient 55 year-old with left eye blurred vision and left dull headache for 2 days. 8 months ago his right arm was in weakness in 2 hours. History notes no FAST, without HTA, DM, except smoking for 30 years.
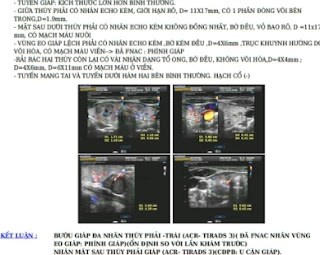
Brain MRI notes left brain ischemia at occipital region in small area and leukoaraiosis.
Vascular ultrasound notes plaque of the left ICA from its origin to occlude all its length and cause no ICA flow; and the left central retinal artery flow decreases.
Because of the ipsilateral ICA occlusion, the left ECA flow becomes internalization.
CTA notes the left ICA occlusion and the left middle cerebral artery is enhanced from the left anterior cerebral artery.
CASE 2:
A HTA male patient 63 year-old with spontaneous loss memory after a critical headache for 6 days. His history is smoking and alcohol beverage for 40 years. No FAST. No loss vision.
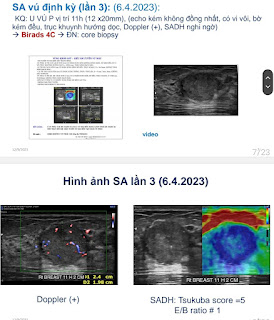
Vascular ultrasound notes plaque at the right ICA origin which narrows up 90% lumen and total left ICA occlusion (NASCET), ICA/CCA ratio> 2.
Brain MRI shows large cerebral ischemia, occlusion of the left middle cerebral artery and the left ICA.
FAST scale and types of diagnostic neuroimaging (vascular ultrasound, CTA and MRI) take theirs roles in cerebral ischemia and stroke.
REFERENCES: [for vascular ultrasound]